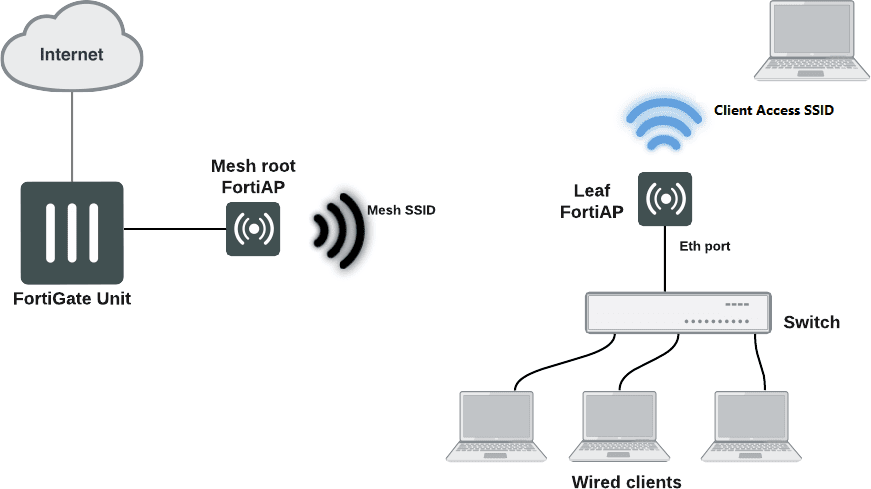
In this article we'll share some of our infallible tips for properly configuring your Wifi network, as well as how to get better performance from your wireless network using the FortiAP: Access Point from Fortinet
Summary
High-density environments always require special attention. For FortiAPs of FortinetI would like to share the following points and recommendations:
- CPU utilization due to high layer 2 traffic
- Tx power settings
- Avoid interference between channels
- Split use of 2.4 GHz (30%) and 5 GHz (70%)
- Avoid low transmission rates (802.11b)
- Activate LLDP
- Use the VLAN pool when available
- Every client and access point on the same channel competes for time to talk
- All clients and access points on overlapping channels talk to each other
- Non 802.11 compete for medium access
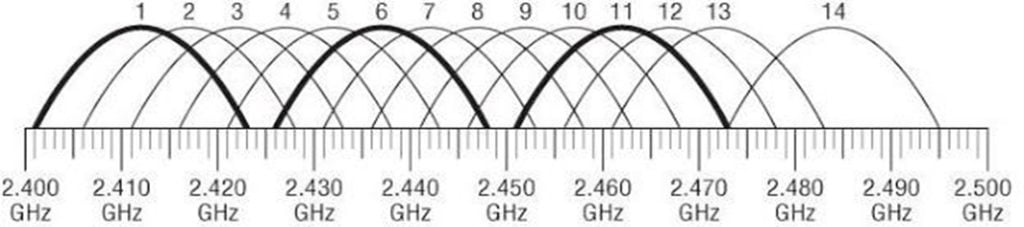
The design of the 2.4 GHz band is always a challenge, problems such as co-channeling and high channel utilization are common.
Today, the power control of the access point is managed by the FortiGateWhen you configure the FortiAP profiles, you get the following Radio Configuration screen:
Best 5ghz Channel
Adjusting Channel Distribution - 5GHz in FortiAP
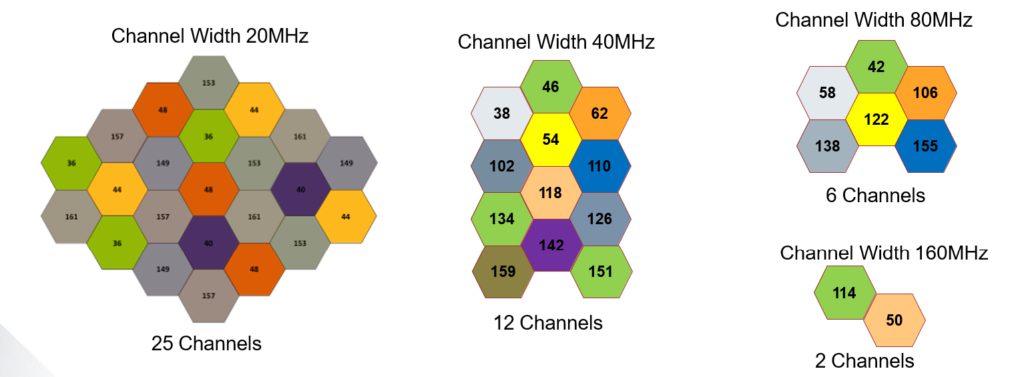
Designing the 5GHz channel is easier if you use the 20MHz channel width.
Common problems
Common Interference Problems between Wireless Channels
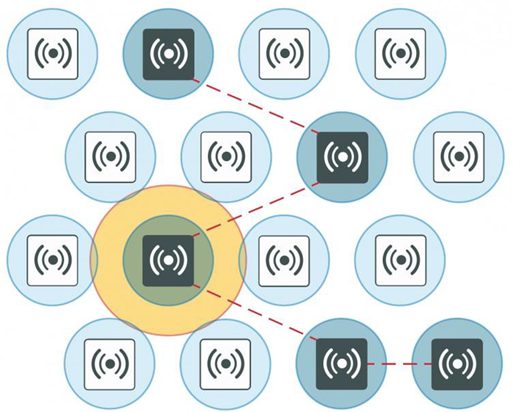
The interference zone can be twice the radius of the signal and the signal at its edge can be -67dBm.
Reducing co-channel interference in your Fortinet FortiAP
For best results, use a honeycomb pattern as a deployment strategy. The idea is to stagger the repeated channels further apart to avoid interference.
TXPower - Less is More (best quality)

- Don't abuse high energy levels, only for specific cases such as PtP is it recommended.
- Try using the automatic power control for 2.4 GHz between 4 and 7 dBm and for 5 GHz between 12 and 20 dBm.
- Use more power on 5GHz channels than on 2.4Ghz channels. Otherwise, Band Steering may not work as expected.
A large proportion of users are still connected to 2.4GHz networks and never connect to 5GHz. - Remember that the wavelength of 2.4 GHz is twice as long as 5 GHz. - 10dBm of 2.4GHz is not the same as 10dBm of 5Ghz - maybe 3 times as much!
TX Power Control - Auto or Manual in AP
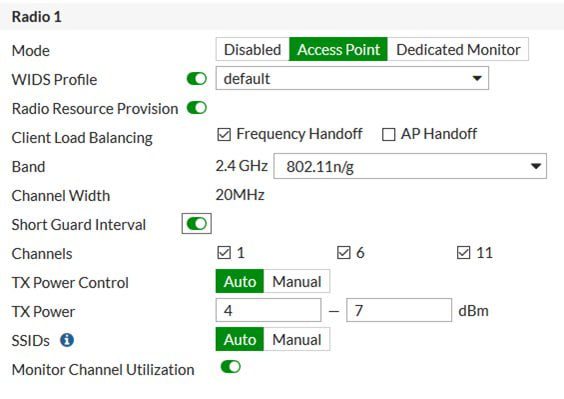
- Auto - You can set the range for minimum and maximum dBm power.
- Manual - Choose the percentage of energy you would like to use. Now the AP will use the static power output.
Power output: TIP2.4GHz - 4dBm to 7dBm 5GHz - 12dBm to 15dBm.
Disable the 802.11b protocol
Disable lower data rates for 802.11a, g, n
Why Optimize DARRP?
- By default, done every 30 minutes (1800s)
- In large networks with many radios and stations, this can cause lengthy calculations, and can also cause multiple channel changes throughout the day (while the Rogue APs roam).
Important tip: Set computing times statically during periods of low traffic
config wireless-controller timers set darrp-optimize 0
set darrp-day sunday monday tuesday wednesday thursday friday saturday
set darrp-time "22:00" "06:00"
end
The 2.4 GHz band is largely "overused".
- Activating frequency handoff encourages customers to use 5GHz
- Faster transfer rate
- No interference
Broadcast Suppression
- Broadcast suppression prevents local network interfaces from being interrupted by broadcast storms.
- Broadcast storm occurs when broadcast or multicast packets flood the subnet, creating excessive traffic and impairing network performance.
- Enabling Broadcast suppression will help prevent ARP or DHCP broadcast messages from being carried to other access points with the same SSID.
- Errors in protocol-stack implementation or network configuration can also cause broadcast storms.